Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder

What is Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder ?
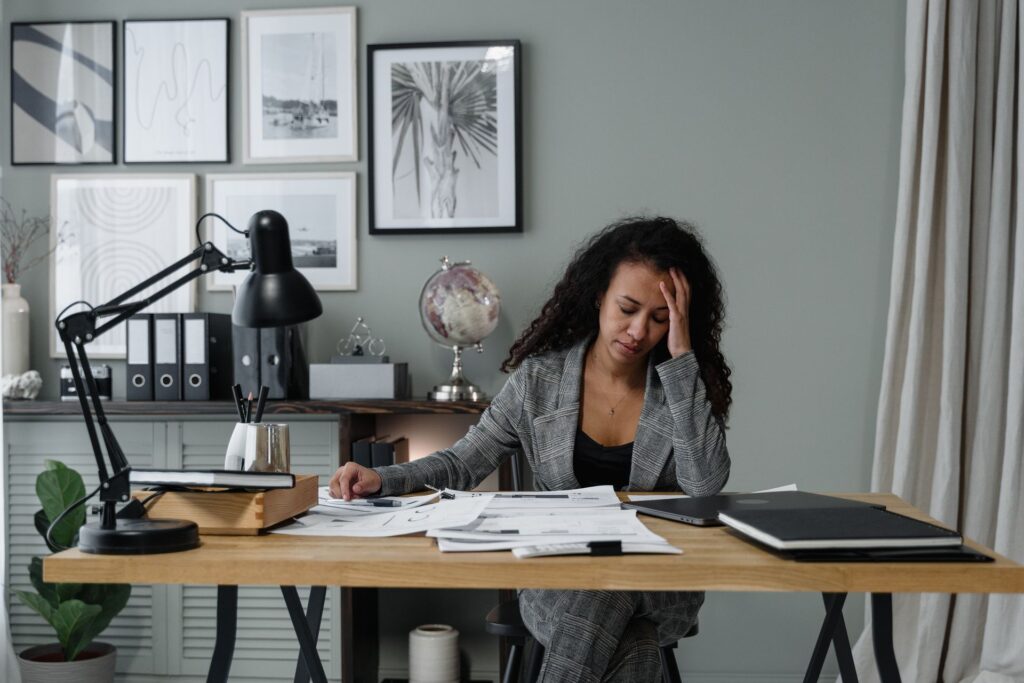
PMDD is a severe form of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) that causes intense mood changes, irritability, and physical symptoms in the days leading up to your period. Unlike PMS, PMDD can disrupt daily life, affect relationships, and take a toll on your emotional well-being.
Common symptoms include mood swings, sadness, irritability, fatigue, and physical discomfort like cramps or headaches. PMDD is linked to hormonal fluctuations and sensitivity to changes in serotonin levels. Recognizing the connection between your body and emotions is the first step toward finding relief and improving your quality of life.
Signs You May Be Experiencing Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
Frequently Asked Questions About Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder Therapy
How does therapy help with PMDD?
Therapy offers a supportive space to address the emotional and physical challenges of PMDD. You’ll learn coping techniques to improve mood regulation, reduce stress, and manage symptoms more effectively during the premenstrual phase.
What type of therapy works best for PMDD?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is highly effective for managing mood swings by identifying and changing negative thought patterns. Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) helps relieve physical symptoms and promote relaxation through breathing exercises and meditation.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) focuses on accepting emotional discomfort without letting it take control. Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) can also help if mood changes are affecting relationships, offering tools to improve communication and navigate conflict.
How soon can I start therapy?
With ReachLink, you can start therapy within 48–72 hours of being matched with a licensed therapist who understands PMDD.
Is therapy covered by insurance?
Yes! ReachLink works with many insurance providers and offers affordable self-pay options, making therapy accessible for everyone.
Personalized Therapy for Lasting Relief.
Individual Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Group Therapy
Couples/Family Therapy
What Our Clients Are Saying
Why Choose ReachLink for Your Mental Health Journey?
Personalized Therapist Matching

Affordable
Options
Fast Access
to Care

Licensed
Therapists